Imagine you’re driving a high-performance car – sleek design, powerful engine, all the bells and whistles. But the steering wheel is loose, the gauges are not functioning properly, and the controls are scattered. No matter how impressive the car itself is, the driving experience will leave you wanting to pull over.
Here’s the thing: In today’s digital landscape, with over 2.8 million mobile apps available on the Google Play Store alone [Source: statista.com], user experience (UX) design isn’t a luxury, it’s the difference between success and obscurity. It’s the bridge that connects a product’s technical capabilities to a user’s intuitive understanding and enjoyment.
Why is UX Important in Product Development?
By integrating UX design principles, models and the design thinking process, software development companies can create products that are:
More Usable: Easy to learn and use, reducing frustration and increasing user satisfaction.
More Engaging: A well-designed product that considers psychology and evokes positive emotions keeps users engaged and coming back for more.
More Successful: Products that meet user needs and are enjoyable to use are more likely to be successful in the market.
Reduced Development Costs: UX helps identify usability issues early, reducing the need for costly rework later in software product development. Usable products also require less customer support, further reducing costs.
7 UX Design Best Practices for Successful Product Development
1. From Features to Users
Traditionally, product development was centered on functionality. But UX design goes beyond functionality, prioritizing the user’s perspective. It asks: what are user needs, pain points, and motivations? How can we make using this product a smooth, enjoyable experience? By understanding these aspects, UX designers craft products that are not just functional but intuitive and enjoyable to use.
2. The Power of User Research
UX design is driven by empathy. Through research methods like surveys and user interviews, designers gain valuable insights into user behavior and thought processes. This knowledge is then translated into a product that anticipates user needs and creates a seamless user journey.
3. The Psychology Behind the Design
Visual elements play a significant role in UX design. Color, layout, and typography are carefully considered to create a product that feels not just aesthetically pleasing, but also trustworthy and user-friendly. For instance, color theory influences user emotions and can be leveraged to create a calming or energetic user experience.
4. The Design Thinking Process:
There’s no magic formula for UX design, but many designers utilize the design thinking process. This iterative approach involves brainstorming solutions, creating prototypes (think low-fidelity sketches or mockups), and crucially, testing these prototypes with real users. This feedback loop allows for continuous refinement, ensuring the final product resonates with the target audience.
5. UX Design Frameworks:
Several UX design tools/frameworks provide structure and guidance for the design process. Here are two popular examples:
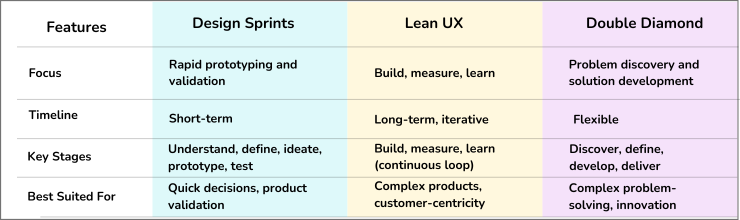
Double Diamond: This iterative model emphasizes divergence and convergence throughout the design process. The first diamond represents the research phases (discover and define), where UX designers gather information and identify the core problem. The second diamond focuses on solutions (develop and deliver), where designers brainstorm ideas, prototype, and test solutions with users.
Google Design Sprints: This model condenses the design thinking process into a fast-paced workshop typically lasting one week. Google Design Sprints involve cross-functional teams working collaboratively to tackle complex design challenges. The process is divided into phases like understanding the problem, sketching solutions, prototyping, and testing with users.
Lean UX: Build, Measure, Learn: Lean UX is a customer-centric approach to product development that emphasizes building, measuring, and learning. It focuses on creating minimum viable products (MVPs) and iterating based on user feedback.
6. Learning from Failure:
It’s important to remember that failure is an inherent part of UX design. Usability testing often reveals flaws in design assumptions. However, these failures are valuable learning opportunities. By embracing a culture of experimentation and iteration, UX designers can continuously improve their solutions based on user feedback.
7. The User-Centered Advantage
By prioritizing UX design, companies can create products that boast not only functionality but also user engagement and satisfaction. This translates to a loyal customer base and a thriving business.
Here are 5 examples of UX design principles in action for everyday software used in many industries:
1. Quickbooks:
Keyboard Shortcuts: Many accounting software programs like Quickbooks allow users to assign keyboard shortcuts for frequently used functions. This reduces reliance on the mouse and saves time for repetitive tasks. (UX Principle: Efficiency)
2. Atlassian Jira:
Drag-and-Drop Functionality: Project management tools like Jira often utilize drag-and-drop functionality to move tasks between stages in a workflow. This allows for a more intuitive visual representation of project progress. (UX Principle: Learnability & User Control)
3. Microsoft Office Suite
Contextual Menus: Programs like Word or Excel display contextual menus that change depending on the selected object or location. This reduces cognitive load by presenting only relevant options at the right time. (UX Principle: Focus & User Context)
4. Slack
Search Functionality: Collaboration tools like Slack prioritize powerful search functionality to quickly find past conversations, files, or information. This saves users time from manually scrolling through long chat histories. (UX Principle: Findability & Efficiency)
5. Google Chrome
Customizable Toolbar: Many software programs, including web browsers like Chrome, allow users to personalize their interface by adding or removing buttons from the toolbar. This caters to individual preferences and workflows. (UX Principle: User Control & Accessibility)
In conclusion, UX design has transformed product development from a purely technical process to a user-centered approach. By prioritizing user needs, emotions, and leveraging tools like design sprints and the design thinking process, UX design helps create products that are not only functional but also successful and cost-effective. While failures are inevitable, they provide valuable learning opportunities that can be used to create better products.
The post The Role of UX in Product Development appeared first on ISHIR | Software Development India.





