Managing workloads in modern analytics environments is not keeping systems running, it’s about making sure the right jobs get the right resources at the right time. As organizations move analytics to the cloud, powered by Kubernetes, balancing workloads across computer resources becomes a critical challenge.
That’s where SAS Viya Workload Management (WLM) comes in. By extending Kubernetes’ native scheduling and workload orchestration, SAS Workload Management ensures jobs run efficiently, users get predictable performance, and administrators maintain visibility and control.
This post, will break down what SAS Workload Management is, how it works, and why it’s a game-changer for SAS Viya environments.
What is SAS Workload Management?
SAS Workload Management is a framework that distributes and balances SAS computing tasks across Kubernetes clusters. It builds on Kubernetes’ workload orchestration but adds intelligence for SAS use cases.
With Workload Management, administrators can:
- Define job priorities by user, group, or workload type.
- Optimize compute resource usage.
- Prevent system overload.
- Ensure that critical work gets done quickly.
The result is a smarter, policy-driven approach to managing complex analytics environments.
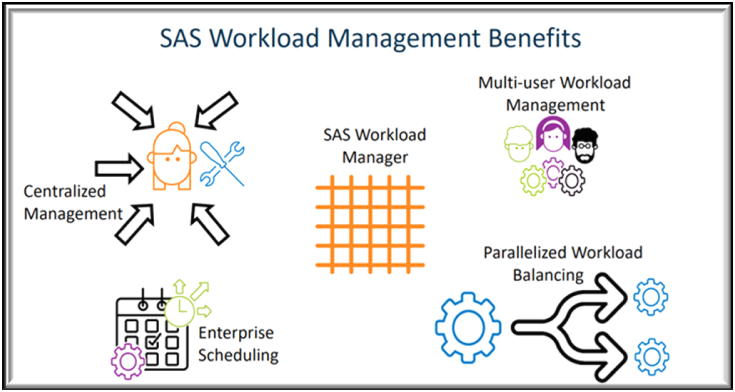
Key Features of SAS Workload Management
- Centralized Management: Administrators can centrally define policies that align with business goals. For example, critical users or workloads can be prioritized to ensure they always receive the resources they need. Policies also extend monitoring capabilities beyond Kubernetes admins—SAS administrators and even end-users can view and track their own jobs.
- Multi-User Workload Balancing: In multi-user environments, job distribution is crucial. SAS Workload Management automatically directs jobs to the best available host, preventing bottlenecks. By avoiding situations where too many jobs run on a single node, the system ensures timely job completion across all users.
- Parallelized Workload Execution: Traditional SAS programs are executed line by line. However, many steps in workflow are independent and can be executed simultaneously. With Workload Management, independent steps can be run as separate jobs in parallel, significantly reducing execution time compared to serial processing.
- Enterprise Scheduling: While Kubernetes offers basic scheduling, SAS Workload Management introduces policy-driven scheduling. Jobs are not just queued, they’re executed on the most appropriate host, increasing the likelihood of on-time completion.
- High Availability & Scalability: SAS Workload Management leverages Kubernetes to provide resiliency and elasticity. Jobs can automatically restart from their last checkpoint, ensuring business continuity even after interruptions. Additionally, clusters can scale up or down dynamically based on demand.
- Monitoring & Administration: Administrators aren’t left in the dark. Through the SAS Environment Manager and dashboards in Grafana, SAS Workload Management offers detailed monitoring of jobs, queues, and hosts. Unlike Kubernetes’ general metrics, these dashboards deliver SAS-specific insights.
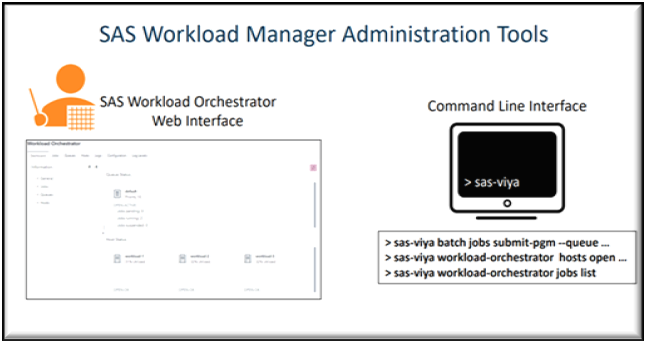
Administration Tools
Administrators can interact with SAS Workload Management through two main tools:
- SAS Environment Manager: Provides a graphical interface to monitor and manage jobs, queues, and hosts. Both administrators and users can access dashboards tailored to their roles. SAS Workload Management | SAS
- Command Line Interface (CLI): Offers flexibility for automation and scripting. Administrators can use CLI plugins to manage workloads remotely, making it easy to integrate into existing DevOps processes. SAS Viya Platform: Using the Command-Line Interface
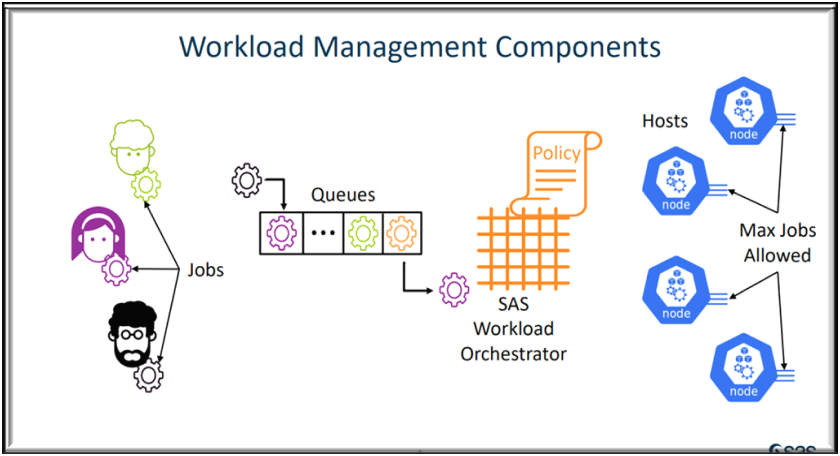
Components of SAS Workload Management
These are the key components:
- Workload Orchestrator: The central brain that manages, monitors, and collects data on jobs and hosts.
- Jobs: Units of work submitted by users. Each job has states like RUNNING or COMPLETED and runs in its own Kubernetes pod.
- Queues: Containers where jobs wait before being dispatched. Queues are governed by policies and priorities.
- Policies: Rules that control how workloads are dispatched, ensuring resources are allocated fairly and strategically.
- Hosts: Kubernetes nodes where jobs run. Each host has limits on how many jobs it can process concurrently.
Together, these components create a dynamic, policy-driven environment for managing SAS workloads.
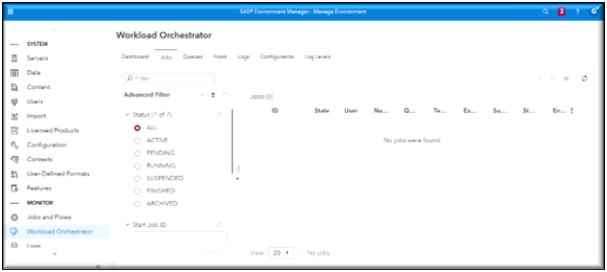
Workload Manager Dashboard page
Workload Manager Jobs page
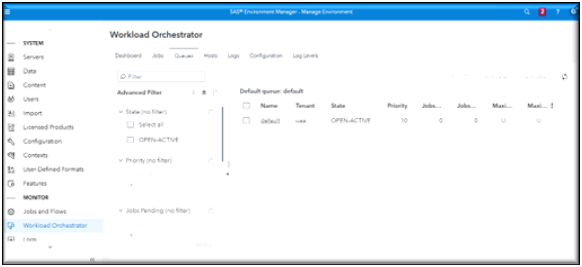
Workload Manager Queue Page
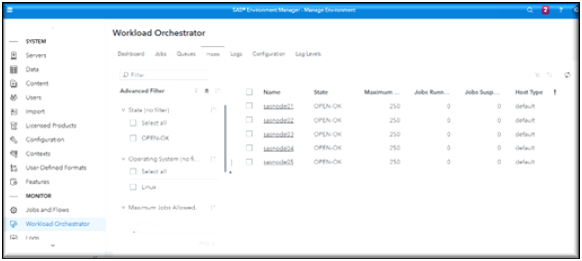
Workload Manager Host Page
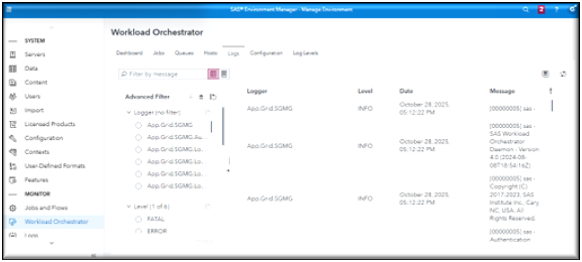
Workload Manager Logs page
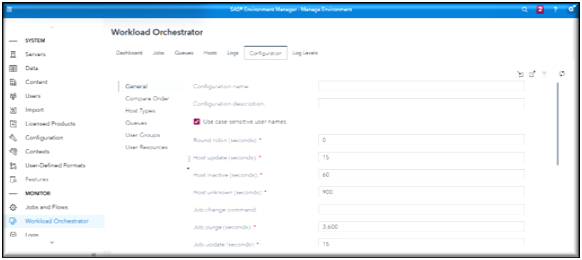
Workload Manager Configuration page
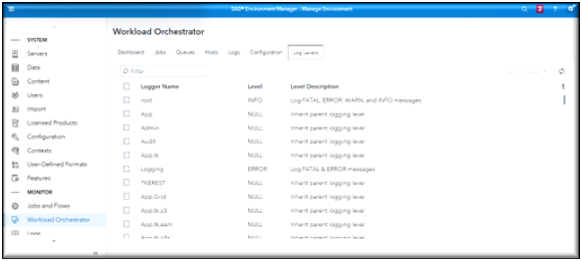
Workload Manager Log Levels page
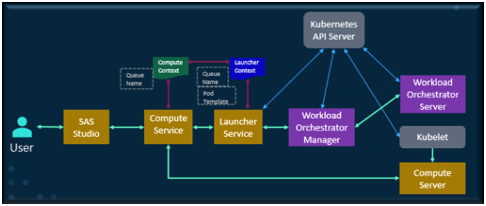
How SAS Workload Management Works.
Here is what happens behind the scenes when a SAS job is submitted:
- A user submits a job through a service like SAS Studio.
- The job is sent to a queue, where it is prioritized relative to other jobs.
- The Workload Orchestrator evaluates available Kubernetes nodes and selectsthe best host based on resources and policies.
- The job is dispatched to the chosen host and executed in a pod.
- If resources are unavailable, the job waits or in some cases, a lower-priority job may be preempted.
- Once complete, the pod is shut down, freeing resources for future jobs.
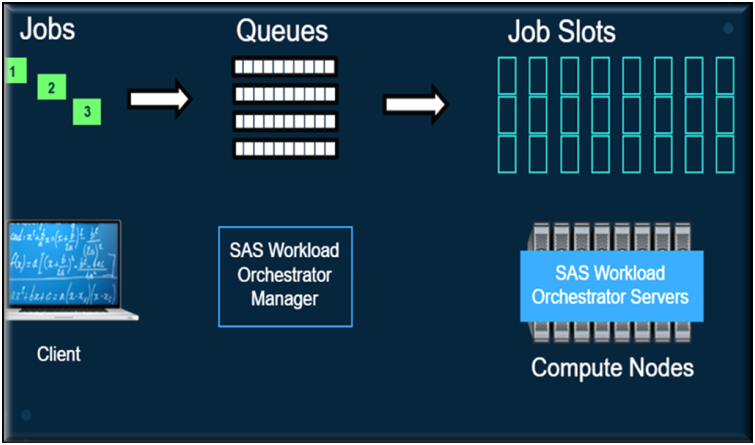
Flow of how Workload Manager works:
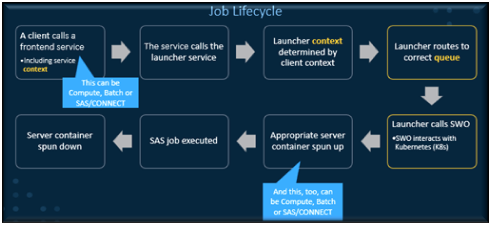
Job Lifecycle
This is an example of the life cycle of a Viya Job once it is submitted to Workload manager.
High-level flow
This is an example of a Viya Job flow once it is submitted to Workload manager.
SAS Viya Workload Management vs. SAS 9 Grid Manager
If you have SAS 9.4 Grid Manager, this may all sound familiar. SAS 9.4 Grid Manager and Viya Workload Manager share the same fundamental mission, to orchestrate, balance and prioritize SAS Jobs across SAS computing resources.
The main difference is that SAS 9.4 Grid Manager was built for traditional on premises clusters, while Viya 4 Workload Manager is Kubernetes-native, making it more flexible for cloud and hybrid deployments.
For organizations migrating from SAS 9 Grid Manager, Workload Management in SAS Viya will feel familiar but more modern.
- Both systems balance workloads and manage resources.
- SAS Viya WLM leverages Kubernetes, making it more flexible and scalable in cloud-native environments.
- The interface and functionality are designed to ease migration, maintaining a sense of continuity for administrators.
In short, SAS Viya Workload Management is the next step in workload orchestration—built for today’s hybrid and cloud-native analytics environments.
Below is a table for comparison between SAS 9.4 Grid Manager and SAS Viya 4 Workload Manager.
Category
SAS 9.4 Grid Manager
SAS Viya 4 Workload Management
Similarity / Difference
Core Purpose
Distributes SAS jobs across a cluster of servers
Distributes SAS jobs across Kubernetes nodes
✅ Similar – both provide workload distribution
Architecture
Built on traditional cluster/grid infrastructure
Cloud-native, Kubernetes-based orchestration
❌ Difference
Job Distribution
Uses LSF (Load Sharing Facility) or 9.4 (SWO) schedulers to distribute jobs
Uses SAS Workload Orchestrator (SWO) integrated with Kubernetes
✅ Similar in concept, ❌ different implementation
Queues & Policies
Jobs submitted to queues, policies define priorities
Jobs submitted to queues, policies define priorities
✅ Similar
Administration Tools
SAS Management Console (Grid Manager plug-in)
SAS Environment Manager, CLI, Grafana dashboards
❌ Difference
Monitoring
Admins monitor jobs, queues, and nodes via Grid tools
Admins & users monitor jobs, queues, and hosts with Environment Manager
✅ Similar, ❌ difference in tooling
User Access
Centralized control, mostly admin-focused
Broader monitoring: admins, queue admins, end-users can view their own jobs
✅ Similar but Viya is more user-friendly
Parallelization
Supports splitting jobs into multiple sub-tasks for parallel execution
Supports parallelized workloads (independent steps/jobs run in separate pods)
✅ Similar
High Availability
Provides job recovery/failover in case of node failure
Kubernetes-native HA: restarts jobs, Auto scales cluster, ensures continuity
✅ Similar, ❌ Viya has stronger cloud-native resiliency
Scalability
Limited by physical cluster resources
Kubernetes allows elastic scaling (horizontal/vertical)
❌ Difference
Deployment Model
Primarily on-premises clusters
Cloud, hybrid, or on-premises with Kubernetes
❌ Difference
Target Users
Enterprises running SAS 9 workloads on grid
Enterprises moving to SAS Viya cloud-native analytics
✅ Similar audience, ❌ different platform maturity
CAS vs Workload Manager
SAS Viya CAS (Cloud Analytic Service) Think of CAS as a turbo engine bult to crunch huge datasets quickly using in-memory computing. When you use Viya Visual tools such as Visual Analytics, Model Studio, or CAS actions, it takes advantage of CAS.
CAS is the Viya engine where heavy analytics work happens.
- CAS loads your data into memory so it can process your jobs fast.
- It runs calculations, models, and reports.
- The more workers nodes you have, the faster it can run your jobs.
Workload Manager is like a traffic controller or project manager for SAS Jobs that takes advantage of the Compute processing using traditional CPU-based SAS code job execution.
- It decides which jobs run first, and which ones wait.
- It makes sure no single user or job hogs the system.
- It manages queues, priorities, and resources so everything runs smoothly.
- It is built on Kubernetes, which means it can scale up or down automatically in the cloud.
Real-World Benefits
Implementing SAS Workload Management translates into measurable improvements:
- Efficiency: Resources are used optimally, reducing wasted capacity.
Performance: Critical jobs finish faster with prioritization and parallel execution.- Transparency: Administrators and users alike can monitor workloads in real time.
- Resiliency: Built-in high availability keeps business processes running smoothly.
Conclusion
As analytics environments grow in complexity, managing workloads effectively is no longer optional—it’s essential. SAS Viya Workload Management provides the tools and intelligence needed to ensure that jobs are prioritized, resources are optimized, and business-critical tasks are completed without interruption.
Whether you’re migrating from SAS 9 Grid Manager or starting fresh with SAS Viya, Workload Management offers a future-ready solution to workload orchestration.
Since SAS Viya Workload Manager is now standard with Viya 4, now is the time to explore how Viya 4 Workload Management can help you get more value out of your analytics environment.